
In sleep mode, your computer keeps the RAM powered on and doesn’t save the contents of the RAM to your SSD. Is Sleep Better Than Hibernate For Your SSD? So you don’t have to worry too much about SSD wearing due to hibernation. Also, the bigger the SSD, the lower the effect of wearing. So only considering the disk operations for hibernation, the SSD can handle (512/16)*3000 or 96,000 hibernations before hitting the write limits, which translates to approximately 87 years if you hibernate your computer 3 times a day.Īs you can see, hibernating your computer a few times a day won’t degrade your SSD significantly. If your computer has 16 GB of RAM, each hibernation will write at most 16 GB of data to the SSD.
WINDOWS 10 SLEEP VS HIBERNATE FULL
So it will take at least 3,000 full disk writes to cause any issue.įor example, consider a 512 GB SSD rated for 3,000 write cycles per cell. However, most modern SSDs can withstand more than 3,000 write cycles per flash cell. So each hibernation can slightly degrade your SSD due to the additional write load. When you hibernate your computer, it writes the content of the RAM to the SSD. SSDs use flash storage, and flash storage has limited write cycles.
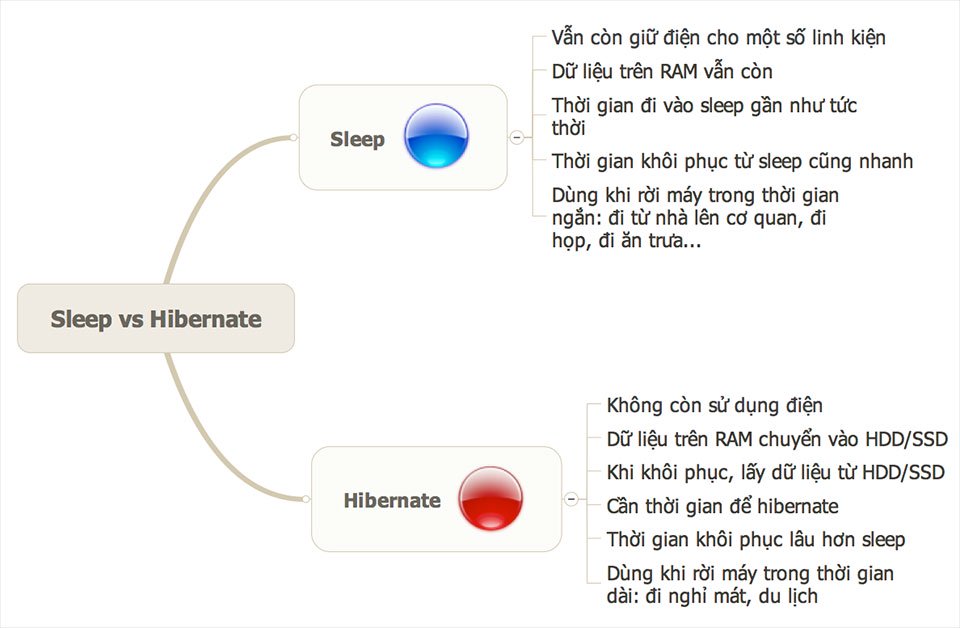
The hibernate option can slightly degrade your computer’s SSD. Because of the saved state of hibernate mode, you can resume the system from where you left off, but it takes longer than sleep mode. When you hibernate your computer, it saves the content on the RAM to the storage drive and then powers off all hardware, including the CPU, GPU, RAM, storage drive, and motherboard. Hibernate is an intermediate step between shutdown and sleep. Because the RAM keeps its state in sleep mode, you can resume your computer quickly and continue your work when you put it to sleep. On the other hand, when you put your computer to sleep, it goes to a lower power mode it turns off the CPU, GPU, and other power-hungry components but keeps the content on the RAM alive by periodically refreshing it. When you shut down your computer, it powers off all its components, including the CPU, GPU, RAM, storage drives, and motherboard all running programs terminate, and your computer has to boot the OS again the next time you turn it on.

WINDOWS 10 SLEEP VS HIBERNATE WINDOWS
Does Windows Fast Startup Degrade Your SSD?.Is Shutdown Better Than Hibernate For Your SSD?.Is Sleep Better Than Hibernate For Your SSD?.Here’s Whether Hibernate Mode Damage SSDs:.To avoid system issues, one must make the system shut down from time to time. While the system is in Hibernate mode, a user will not be able to use the system.Ī Sleeping computer is still working it is running the basic functions behind and using the electricity. The process is stopped, and the work is saved in the RAM memory. Standby (in Windows older version), Suspended to RAM (in Linux), S3 in ACPI Suspended to disk (in Linux), Safe Seep (in Mac), S4 (in ACPI) Preferred when the system is idle for a shorter period of time Generally, when the system is idle for a longer time period and also the rebooting after shutdown will be a time taking process. Wakeup Time for Hibernate vs Sleep mode is less than 100 uS and less than 15 uS, respectively.īelow is the 7 top most comparison: The basis of comparison Between Hibernate vs Sleep mode.Hibernate has a current consumption of less than 300nA, whereas, for the Sleep mode, the current consumption is around less than 2nA.Hibernate mode is useful if you do not want to use your laptop for a longer time, whereas Sleep mode is useful if it is suspended for a shorter time.No power is needed to maintain in hibernate mode, but a small amount of power is needed to maintain the sleep mode (as the work is saved in RAM).Computer works are saved in the hard disk in Hibernate mode, whereas in Sleep mode, the work is saved is saved in the RAM.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
